leetcode 283: 移动零
Given an array nums, write a function to move all 0’s to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
- 思路一: python的暴力美学 复杂度$O({N}^2)$
class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
origin_len = len(nums)
idx = 0
while idx < origin_len:
if nums[idx] == 0:
nums.pop(idx)
nums.append(0)
origin_len -= 1
else:
idx += 1
- 思路二 :两次遍历 时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 创建两个指针i和j,第一次遍历的时候指针j用来记录当前有多少非0元素,i逐个进行遍历,每遇到一个非0元素就放到nums[j]中,然后j加一,第一次遍历完后,j指针的下标就指向了最后一个非0元素下标。
- 第二次遍历的时候,起始位置就从j开始到结束,将剩下的这段区域内的元素全部置为0。
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
if not nums:
return 0
# 第一次遍历的时候,j指针记录非0的个数,只要是非0的统统都赋给nums[j]
j = 0
for i in xrange(len(nums)):
if nums[i]:
nums[j] = nums[i]
j += 1
# 非0元素统计完了,剩下的都是0了
# 所以第二次遍历把末尾的元素都赋为0即可
for i in xrange(j,len(nums)):
nums[i] = 0
- 思路三 依次遍历
- 参考了快速排序的思想,快速排序首先要确定一个待分割的元素做中间点x,然后把所有小于等于x的元素放到x的左边,大于x的元素放到其右边。 这里我们可以用0当做这个中间点,把不等于0(注意题目没说不能有负数)的放到中间点的左边,等于0的放到其右边。 这的中间点就是0本身,所以实现起来比快速排序简单很多,我们使用两个指针i和j,只要nums[i]!=0,我们就交换nums[i]和nums[j]。
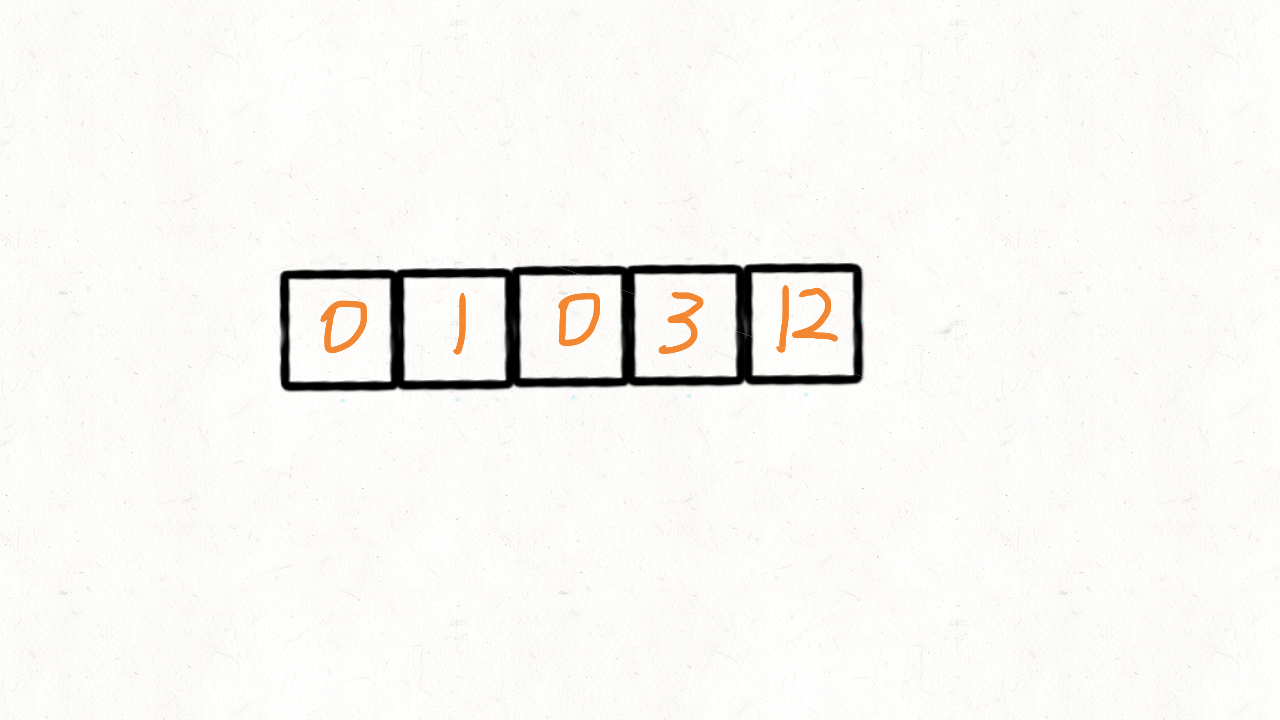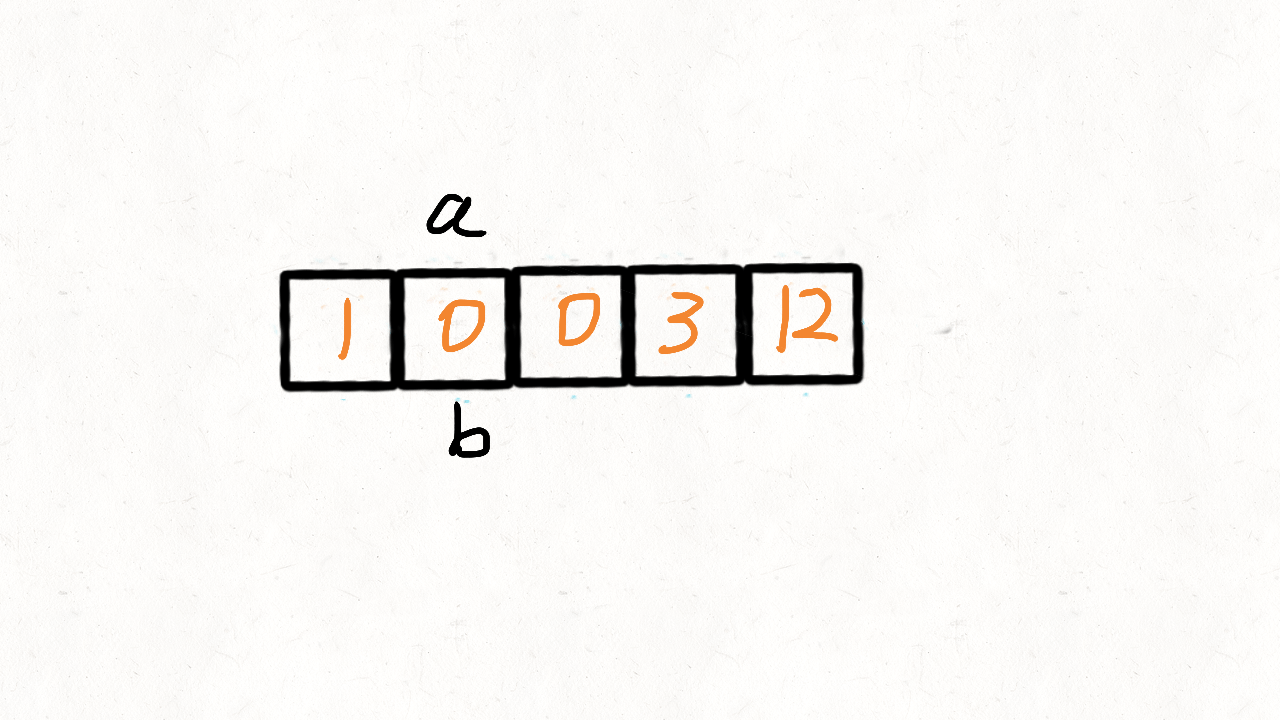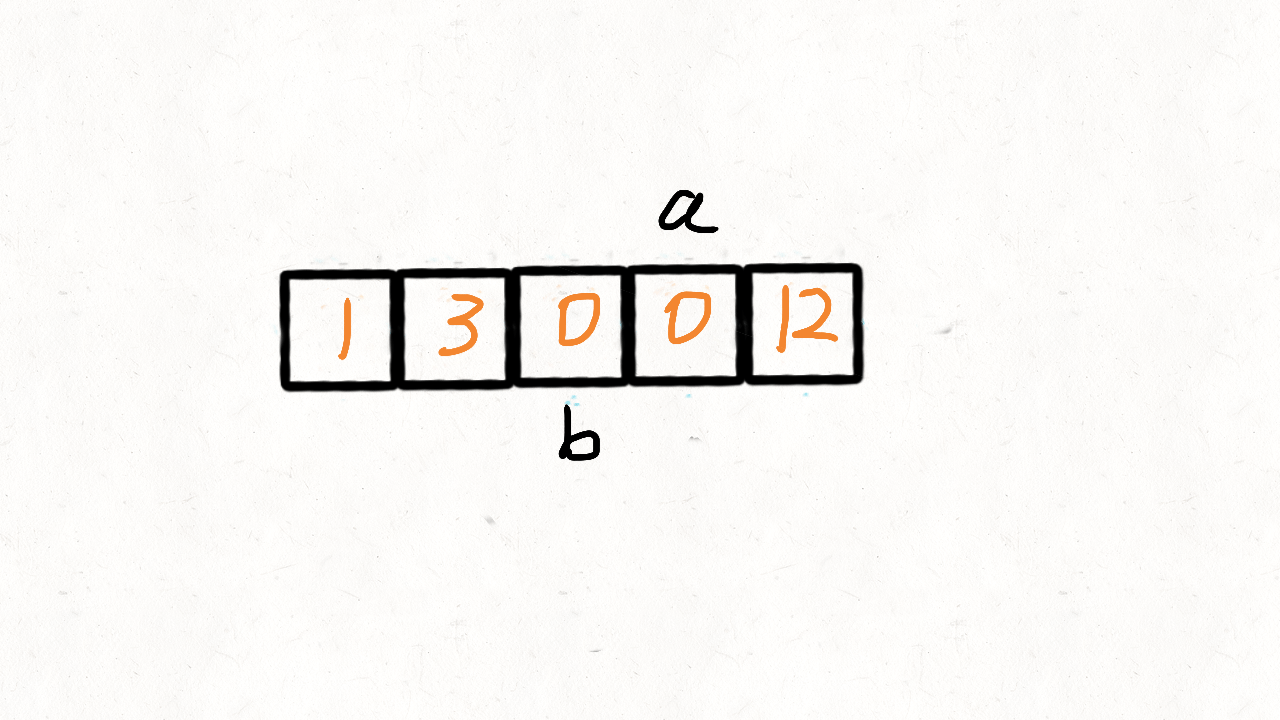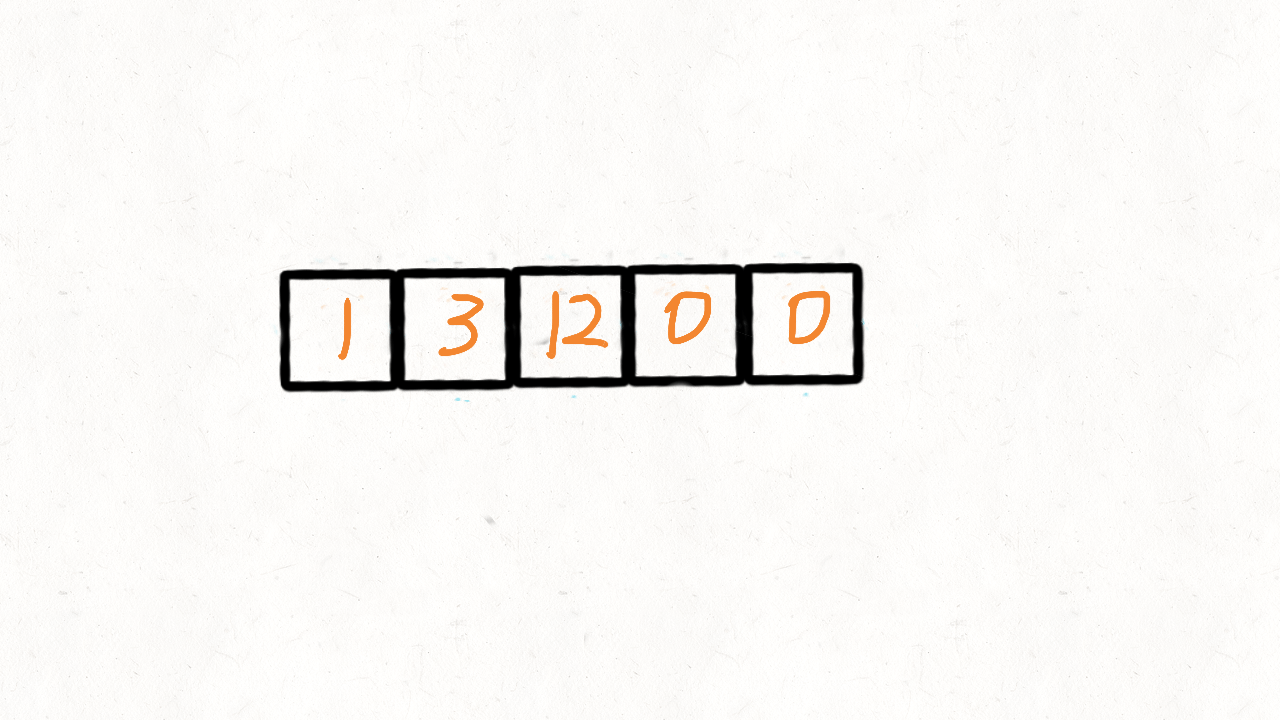
class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
if not nums:
return nums
j = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[i],nums[j] = nums[j],nums[i]
j += 1
leetcode 27: 移除元素
Given an array nums and a value val, remove all instances of that value in-place and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn’t matter what you leave beyond the new length.
Example 1:
Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
- 思路一 快慢指针法,快指针在前面遍历,遇到满足条件的(!=val)覆盖掉慢指针的内容,两指针加一处理下一个位置,不满足条件时快指针加一,慢指针不动。
class Solution:
def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int:
if not nums:
return head
j = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i]!=val:
nums[j] = nums[i]
j += 1
return j
-
思路二 依旧是双指针法,当删除的元素较少时比较合适
- 一个指针正向遍历,每次遇到val时修改其值为数组末尾元素值,指向最后一个元素的指针前移一位。注意:正向指针此时不向前,因为换过来的节点也可能是val。不是val节点时向前移。
class Solution: def removeElement(self, nums: List[int], val: int) -> int: if not nums: return 0 i,n = 0 , len(nums) while i < n: if nums[i] == val: nums[i] = nums[n-1] n -= 1 else: i += 1 return n
leetcode 26:删除排序数组中的重复项
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,2],
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
- 思路 同上,双指针
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) <=1:
return len(nums)
#慢指针,0处必然不重复,赋值后自增
j = 1
#i从1开始,和之前的比较,如果不相等需要赋值给慢指针
#最终满指针的值就是新数组长度
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
if nums[i] != nums[i-1]:
nums[j] = nums[i]
j += 1
return j
leetcode 80: 删除排序数组中的重复项2
[中等]Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that duplicates appeared at most twice and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3],
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 1, 1, 2, 2 and 3 respectively.
It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
-
思路:不能类似上道题那样比对,后面的值赋值给前面可能导致出现多个重复的问题
[1,1,1,2,2,3] -> [1,1,2,3] 第二个2会被删除 -
思路一:基于python的pop(i)就地对元素进行删除,需要用count来统计该元素出现次数。
- 时间复杂度:让我们看看最耗时的操作是什么: 我们必须遍历数组中的所有元素,若数组中有 N 个元素,则花费的时间为O(N)。 删除多余的重复项,del 操作也是 O(N)。 最糟糕的情况是数组中的元素都相同,则我们需要执行N-1次的删除操作,则需要花费 $O(N^{2})$ 总的复杂度:$O(N) + O(N^2) = O(N^2)$
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) < 3:
return len(nums)
i = 1
count = 1 #计数大于2时删除元素
while i < len(nums):
if nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
count += 1
else :
count = 1
if count >2:
nums.pop(i)
else:
i += 1
return i
- 思路二 覆盖多余重复项,类似上题的做法,但引入count计数器,同样是满足条件时进行覆盖。
class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) < 3:
return len(nums)
j = 1
count = 1
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
count = count+1 if nums[i]==nums[i-1] else 1
if count <= 2:
nums[j] =nums[i]
j += 1
return j
leetcode 88: 合并两个有序数组
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:
The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively. You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is greater or equal to m + n) to hold additional elements from nums2.
Example:
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
- 双指针法,从前往后遍历需要移动大量的节点,因此不妨考虑从后往前遍历的方法,以刚好容纳m+n个节点的位置开始遍历,同样从两个数组的末尾开始比较。
class Solution:
def merge(self, nums1: List[int], m: int, nums2: List[int], n: int) -> None:
#长度刚好容纳m+n个值
cur = m+n-1
i,j = m-1,n-1
while i>=0 and j>=0:
if nums1[i] >= nums2[j]:
nums1[cur] = nums1[i]
i -= 1
else:
nums1[cur] = nums2[j]
j -= 1
cur -= 1
#nums2剩下 把剩下的拼到nums1里
if j >= 0:
while j >=0 :
nums1[cur] = nums2[j]
j -= 1
cur -= 1
leetcode 167: 两数之和 2
Given an array of integers that is already sorted in ascending order, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number.
The function twoSum should return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to the target, where index1 must be less than index2.
Note:
Your returned answers (both index1 and index2) are not zero-based. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 2
- 思路:用dict存储 值-索引
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, numbers: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
vals = {}
for i in range(len(numbers)):
if target-numbers[i] in vals.keys():
return [vals[target-numbers[i]]+1,i+1]
else:
vals[numbers[i]] = i
*leetcode 75: 颜色分类
[中等]Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white and blue.
Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue respectively.
Note: You are not suppose to use the library’s sort function for this problem.
Example:
Input: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
Output: [0,0,1,1,2,2]
Follow up:
A rather straight forward solution is a two-pass algorithm using counting sort. First, iterate the array counting number of 0’s, 1’s, and 2’s, then overwrite array with total number of 0’s, then 1’s and followed by 2’s. Could you come up with a one-pass algorithm using only constant space?
- 思路: 荷兰国旗问题,用三个指针(p0, p2 和curr)来分别追踪0的最右边界,2的最左边界和当前考虑的元素,沿着数组移动
curr指针,若nums[curr] = 0,则将其与nums[p0]互换;若nums[curr] = 2,则与nums[p2]互换。 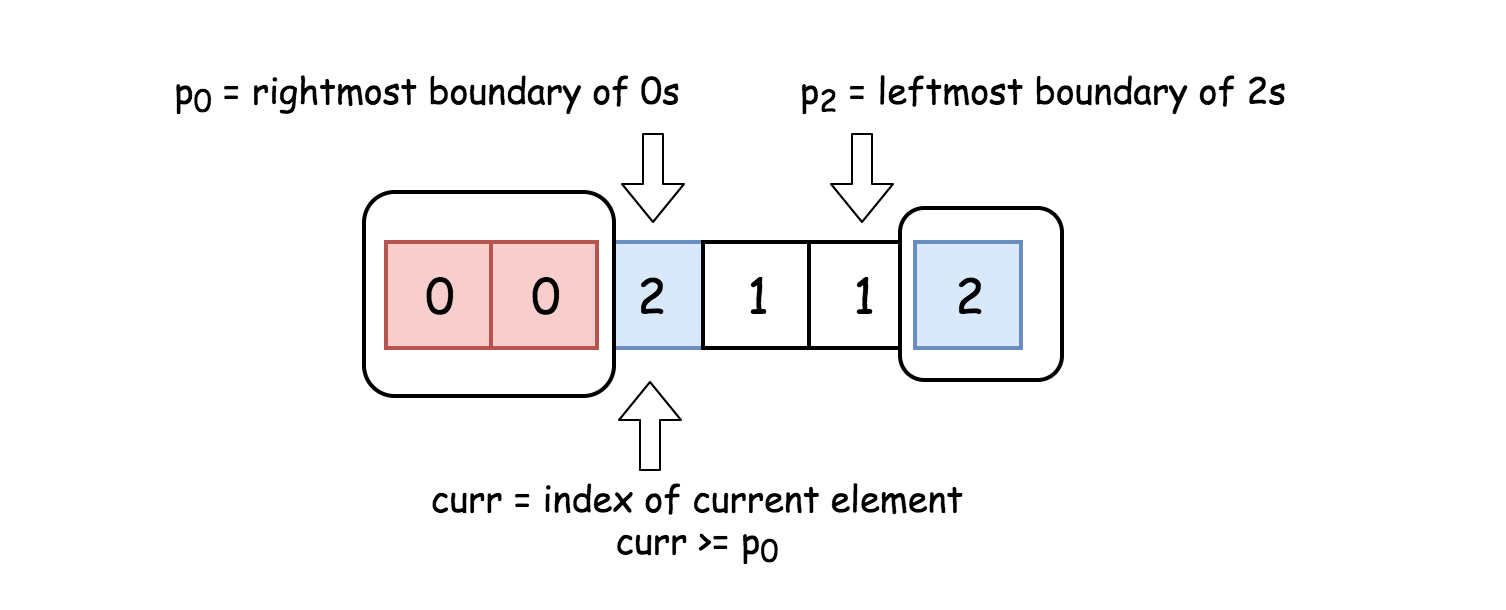
- 算法
- 初始化0的最右边界:p0 = 0。在整个算法执行过程中 nums[idx < p0] = 0.
- 初始化2的最左边界 :p2 = n - 1。在整个算法执行过程中 nums[idx > p2] = 2.
- 初始化当前考虑的元素序号 :curr = 0.
- While curr <= p2 :
- 若 nums[curr] = 0 :交换第 curr个 和 第p0个 元素,并将指针都向右移。
- 若 nums[curr] = 2 :交换第 curr个和第 p2个元素,并将 p2指针左移 。新移过来的元素需要在经历一次判断。
- 若 nums[curr] = 1 :将指针curr右移。
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
p0 , cur , p2 = 0 , 0 , len(nums)-1
while cur <= p2:
if nums[cur] == 0:
nums[p0],nums[cur] = nums[cur],nums[p0]
p0 , cur = p0+1 , cur+1
elif nums[cur] == 2:
nums[p2],nums[cur] = nums[cur],nums[p2]
p2 -= 1
else:
cur += 1
*leetcode 215: 数组中的第 k 个最大元素
[中等]Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
Output: 4
Note: You may assume k is always valid, 1 ≤ k ≤ array’s length.
- 思路:对列表建堆,然后逐个弹出来获取第k个值。
- python堆相关库:heapq
- 直接使用列表来创建堆 : heapq.heapify(li)
- 插入、弹出元素: heapq.heappush(li,1) heapq.heappop(li) 每次出来的元素是最小的
- 优先队列queue.PriorityQueue是对heapq的封装,使用(value,content)来作为队列元素,value较大的有较高的优先级,value一样会比较content.
- PriorityQueue 相关函数:put() get() empty()
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
import heapq
heapq.heapify(nums)
#小根堆 倒数第k个元素为正数n-k+1
idx = len(nums) - k + 1
while idx:
val = heapq.heappop(nums)
idx -= 1
return val
- 思路二 快速选择算法
快速选择算法 的平均时间复杂度为$ {O}(N)$。就像快速排序那样,本算法也是 Tony Hoare 发明的,因此也被称为 Hoare选择算法。
本方法大致上与快速排序相同。简便起见,注意到第 k 个最大元素也就是第 N - k 个最小元素,因此可以用第 k 小算法来解决本问题。
- 首先,我们选择一个枢轴,并在线性时间内定义其在排序数组中的位置。这可以通过 划分算法 的帮助来完成。
- 为了实现划分,沿着数组移动,将每个元素与枢轴进行比较,并将小于枢轴的所有元素移动到枢轴的左侧。
- 这样,在输出的数组中,枢轴达到其合适位置。所有小于枢轴的元素都在其左侧,所有大于或等于的元素都在其右侧。
- 这样,数组就被分成了两部分。如果是快速排序算法,会在这里递归地对两部分进行快速排序,时间复杂度为 ${O}(N \log N)$。而在这里,由于知道要找的第 N - k 小的元素在哪部分中,我们不需要对两部分都做处理,这样就将平均时间复杂度下降到 ${O}(N)$。
最终的算法:
- 随机选择一个枢轴。
- 使用划分算法将枢轴放在数组中的合适位置 pos。将小于枢轴的元素移到左边,大于等于枢轴的元素移到右边。
- 比较 pos 和 N - k 以决定在哪边继续递归处理。
本算法也适用于有重复的数组
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums, k):
def partition(left, right, pivot_index):
pivot = nums[pivot_index]
# 1. pivot不用与自身比较,与最后一个元素交换
nums[pivot_index], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[pivot_index]
# 2. 每次有小于pivot的元素时与store交换,最终store在小于pivot和大于pivot的元素分割线上(具体位置跟pivot值选择和元素范围有关),其值为一个大于pivot的值。所以最后与pivot所在位置end的值交换
store_index = left
for i in range(left, right):
if nums[i] < pivot:
nums[store_index], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[store_index]
store_index += 1
# 3. 将pivot移到分割点store
nums[right], nums[store_index] = nums[store_index], nums[right]
return store_index
def select(left, right, k_smallest):
if left == right: # If the list contains only one element,
return nums[left] # return that element
# select a random pivot_index between
pivot_index = random.randint(left, right)
# find the pivot position in a sorted list
pivot_index = partition(left, right, pivot_index)
# pivot左边的都比pivot小,右边都比pivot大,pivot刚好是第k个时
if k_smallest == pivot_index:
return nums[k_smallest]
# pivot 大于k,第k个在左半部分
elif k_smallest < pivot_index:
return select(left, pivot_index - 1, k_smallest)
else:
return select(pivot_index + 1, right, k_smallest)
return select(0, len(nums) - 1, len(nums) - k)
leetcode 11: 盛最多水的容器
给你 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,…,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0)。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
说明:你不能倾斜容器,且 n 的值至少为 2
示例:
输入:[1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
输出:49
我们在由线段长度构成的数组中使用两个指针,一个放在开始,一个置于末尾。 此外,我们会使用变量 maxarea来持续存储到目前为止所获得的最大面积。 在每一步中,我们会找出指针所指向的两条线段形成的区域,更新 maxarea,并将指向较短线段的指针向较长线段那端移动一步。当两边相等时移动哪一个都没影响。
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
maxA = 0
i,j = 0,len(height)-1
while i < j :
_A = (j-i)*min(height[i],height[j])
if _A > maxA:
maxA = _A
if height[i]<height[j]:
i += 1
else :
j -= 1
return maxA
leetcode 209: 长度最小的子数组
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 s ,找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ s 的长度最小的连续子数组。如果不存在符合条件的连续子数组,返回 0。
示例:
输入: s = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
输出: 2
解释: 子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的连续子数组。 进阶:
如果你已经完成了O(n) 时间复杂度的解法, 请尝试 O(n log n) 时间复杂度的解法。
- 思路一 暴力法,逐个子序列遍历找到最短且满足条件的,$O(N)$.
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
min_len = int(1e5)
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i,len(nums)):
#计算i-j之间的所有子序列
sum_val = 0
for k in range(i,j+1):
sum_val += i
if sum_val >= s:
min_len = min(min_len,j-i+1)
break
#j再往后走也不会有长度较短的序列了 遍历下一个i
return min_len
-
思路二 优化的暴力法:使用一个数组来存储每个位置得到的之前值的累加和,通过相减快速得到两个位置之间值的和。
算法 唯一的不同是求子数组的和: 建立一个大小为$ \text{nums}$的向量 $\text{sums}$ 初始化$ \text{sums}[0]=\text{nums}[0]$ 遍历 向量$ \text{sums}$: 更新$ \text{sums}[i] = \text{sums}[i-1] + \text{nums}[i]$ 从i到 j 的和计算方法: $\text{sum}=\text{sums}[j] - \text{sums}[i] +\text{nums}[i]$,其中 $\text{sums}[j] - \text{sums}[i]$是从第 i+1个元素到第 j个元素的和。
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if len(nums) <= 0:
return 0
min_len = int(1e5)
sums = [nums[0]]
#计算sums数组值
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
sums.append(sums[i-1]+nums[i])
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i,len(nums)):
cur = sums[j]-sums[i]+nums[i]
if cur >= s:
min_len = min(min_len,j-i+1)
break
return min_len if min_len != int(1e5) else 0
- 以上两种方法都会超时
- 思路三 双指针法 (滑动窗口法) 一旦知道某个位置开始的子数组不会是最优答案之后就可以移动左端点。用 2 个指针,一个指针left指向数组开始的位置,一个指针i不断遍历,当满足区间内的和 $\text{sum}$大于等于 s 时开始移动left,并不断更新最短的区间长度。当小于s时则移动i指针。 O(N)
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
min_len = int(1e8)
left = 0
sum_val = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
sum_val += nums[i]
while sum_val >= s:
#一直左移left找最短且满足条件的子序列
min_len = min(min_len,i-left+1)
sum_val -= nums[left]
left += 1
return min_len if min_len != int(1e8) else 0
- 思路四 二分查找 对思路2构造的sums数组,其值为递增,可以对其使用二分查找来找到满足条件的最短区间长度。 O(NlogN)
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, s: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
if not nums : return 0
# 求前缀和
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
nums[i] += nums[i - 1]
# 总和都小于 s 时候
if nums[-1] < s: return 0
res = float("inf")
nums = [0] + nums
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] - s >= 0:
# 二分查找 bisect python查找库
loc = bisect.bisect_left(nums, nums[i] - s)
if nums[i] - nums[loc] >= s:
res = min(res, i - loc)
continue
if loc > 0:
res = min(res, i - loc + 1)
return res