从尾到头打印链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,按链表从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
-
列表反转:从头到尾获取链表节点的值并存入list,之后反转list.
-
递归
#solution 1 class Solution: # 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3] def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode): l = [] while listNode: l.append(listNode.val) listNode = listNode.next return l[::-1] #solution 2 def recu(result,listNode): if not listNode: return recu(result,listNode.next) result.append(listNode.val) class Solution: # 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3] def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode): result = [] recu(result,listNode) return result
删除链表中重复的节点
题目描述(同leetcode 83) 中等难度
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5.
- 使用两个指针p、q同时遍历链表,用q与q.next比较判断需要删除的节点,之后使用p.next=q.next删除中间重复的节点。
- 注意点:
- 链表1->1->2类型,在头部重复。添加新的链表表头。
- 链表1->2->2->2类型,大于2个重复结点。使用while循环找到不相同的节点为止。注意:找到后并不是直接链接不相同的结点,因为后面可能同样会出现重复的情况。如:1->2->2->3->3->4,遇到第一个3时不能直接把p.next指向3,而是通过q指针越过之前重复的元素,然后对新的元素进行比较。
- 最后可能存在一个尾节点需要添加。重要:没有这一行会导致p仍然链接一部分原链表节点,q的跳跃没有起到应有的作用。
class Solution:
def deleteDuplication(self, pHead):
# new linklist head
head = ListNode(0)
head.next = pHead
p=head
q = head.next
while q and q.next:
if q.val == q.next.val:
#>=2 same value node,jump these nodes
while q.next and q.val == q.next.val:
q.next = q.next.next
else:
p.next = q
p = p.next
q = q.next
#link last node
p.next = q
return head.next
链表中的倒数第 k 个节点
题目描述
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
- 两个指针head、q,q先走k个节点,之后head与q同时向后遍历,当q指向最后一个节点时head指向倒数第k个节点。
- 注意:k值可能越界
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self, head, k):
q = head
for _ in range(k):
#note : note q.next
if q:
q = q.next
else:
return None
while q:
q = q.next
head = head.next
return head
链表中环的入口节点
题目描述 剑指Offer 23 中等难度 leetcode 142
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点,否则,输出null。
- 思路一:使用set来存储遍历的每一个节点,遇到重复节点则为环的入口。空间复杂度$O(n)$。
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
nodes = set()
while pHead:
if pHead in nodes:
return pHead
else:
nodes.add(pHead)
pHead = pHead.next
return None
-
思路二:
- 使用一块一慢两个指针,如果有环则两个指针会相遇;
- 固定一个指针,单步移动另一个,当其相等时可计算出环的长度$l$;
- 两个指针位置分别设为0和l,以相同速度向后遍历,相遇节点即为环入口节点。
- 注意:各层循环的判定条件,以及对空链表以及长度小于2的链表的判断。
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
if not pHead or not pHead.next or not pHead.next.next:
return None
pslow = pHead.next
pfast = pslow.next
#if exists loop
while pfast != pslow:
#使用较快的指针next来判断是否到链表尾
if not pfast.next or not pfast.next.next:
return None
pfast = pfast.next.next
pslow = pslow.next
#确定存在循环,计算环的长度
length = 1
while pfast.next != pslow:
pfast = pfast.next
length += 1
#两指针从 0和l处开始遍历,相遇时为环的入口
pfast = pslow = pHead
for _ in range(length):
pfast = pfast.next
while pfast != pslow:
pfast = pfast.next
pslow = pslow.next
return pfast
- 思路三 floyd算法
- Floyd 的算法被划分成两个不同的阶段。在第一阶段,找出列表中是否有环,如果没有环,可以直接返回
null并退出。否则,用相遇节点来找到环的入口。 - 给定阶段 1 找到的相遇点,阶段 2将找到环的入口。首先我们初始化额外的两个指针:ptr1指向链表的头, ptr2 指向相遇点。然后,我们每次将它们往前移动一步,直到它们相遇,它们相遇的点就是环的入口,返回这个节点。
- Floyd 的算法被划分成两个不同的阶段。在第一阶段,找出列表中是否有环,如果没有环,可以直接返回
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next or not head.next.next:
return None
slow,fast = head.next,head.next.next
while slow != fast:
if not fast.next or not fast.next.next:
return None
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
fast = head
while fast != slow:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow
反转链表
题目描述
输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
- 初始化一个表头,遍历链表时使用头插入法插入到新表头后面,注意要使用临时变量存储,避免破坏pHead正向的遍历过程。
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
result = ListNode(0)
while pHead:
temp = pHead
pHead = pHead.next
temp.next = result.next
result.next = temp
return result.next
合并两个排序的链表
题目描述
输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
- 先两个同时遍历 知道有一个空为止,之后把非空的连接到新的链表后。
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
result = ListNode(0)
p3 = result
while pHead1 and pHead2:
if pHead1.val < pHead2.val:
p3.next = pHead1
pHead1 = pHead1.next
else:
p3.next = pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
p3 = p3.next
p3.next = pHead1 if pHead1 else pHead2
return result.next
复杂链表的复制
题目描述 剑指Offer 35 中等难度
输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针random指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的head。(注意,输出结果中请不要返回参数中的节点引用,否则判题程序会直接返回空)
- 简单思路:先复制只带next指针的链表,之后对每个节点逐个遍历为其设定特殊指针的指向,时间复杂度为$O(n^2)$。
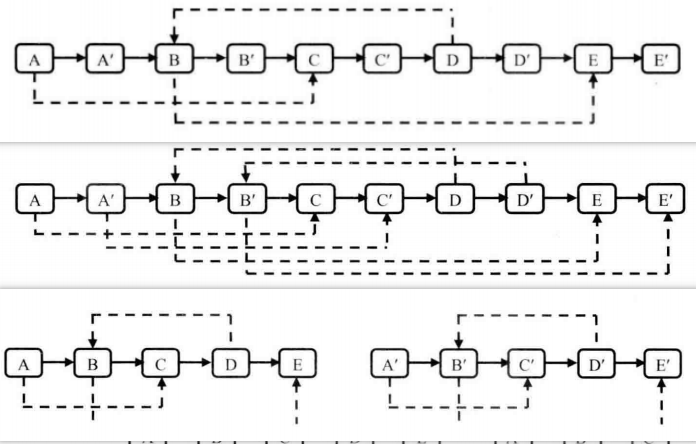
- 优化:三步法
- 在原链表的基础上复制链表,在每个节点后插入一个复制节点;
- 遍历合成的链表,复制random的指向关系;
- 将合成的链表拆成两个新链表。
class Solution:
# 返回 RandomListNode
def Clone(self, pHead):
if not pHead:
return None
#依据next指针拷贝链表
p = pHead
while p:
node = RandomListNode(p.label)
node.next = p.next
p.next = node
p = node.next
#从前往后链接random指针 注意random指针可能为空
p = pHead
while p:
p.next.random = p.random.next if p.random else None
p = p.next.next
#分离两个链表 注意循环体里的做法。两个链表进行分离时的过程
p=pHead
result = p.next
q = result
while p:
p.next = q.next
p = p.next
if not p:
break
q.next = p.next
q = q.next
return result
- 解法二:递归
class Solution:
def Clone(self, head):
if not head: return
newNode = RandomListNode(head.label)
newNode.random = head.random
newNode.next = self.Clone(head.next)
return newNode
两个链表的第一个公共节点
题目描述 剑指Offer 52
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。(注意因为传入数据是链表,所以错误测试数据的提示是用其他方式显示的,保证传入数据是正确的)
- 思路一:公共结点之后两个链表相交,计算两个链表的长度差l,然后较长的链表指针先走l步,之后两指针一块遍历,当其相等时就是公共节点。
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self, pHead1, pHead2):
if not pHead1 or not pHead2:
return None
#计算长度
len1,len2 = 0,0
p,q = pHead1,pHead2
while p:
p = p.next
len1 += 1
while q:
q = q.next
len2 += 1
if len2 > len1 :
pHead1,pHead2 = pHead2,pHead1
#一个先走len1-len2步 之后同步遍历
p,q = pHead1,pHead2
for _ in range(len1-len2):
p = p.next
while p and q and p != q:
p = p.next
q = q.next
return p if p else None
- 思路二:依照栈的后进先出机制,使用两个栈保存链表,在同步弹出,找到不相同的前一个节点为公共节点。
- python的栈 直接使用list,带有append pop函数。
- 队列:可以使用list的append pop(0)但效率低$O(n)$,collections有deque模块,有相应的append、pop、popleft等函数可用作栈、队列。
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self, pHead1, pHead2):
if not pHead1 or not pHead2:
return None
stack1,stack2 = [],[]
while pHead1:
stack1.append(pHead1)
pHead1 = pHead1.next
while pHead2:
stack2.append(pHead2)
pHead2 = pHead2.next
first = None
while stack1 != [] and stack2 != []:
val1 = stack1.pop()
val2 = stack2.pop()
if val1 == val2:
first = val2
return first if first else None
leetcode 206: 反转链表
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL 进阶: 你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题.
- 迭代法见上。
- 递归法:先寻找到最后一个节点,将其连接在head后。
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
# 递归终止条件是当前为空,或者下一个节点为空
if(head==None or head.next==None):
return head
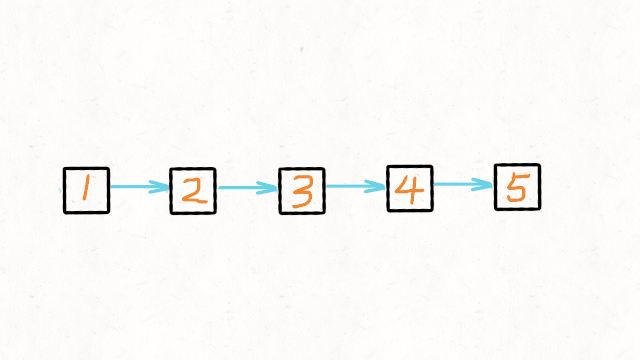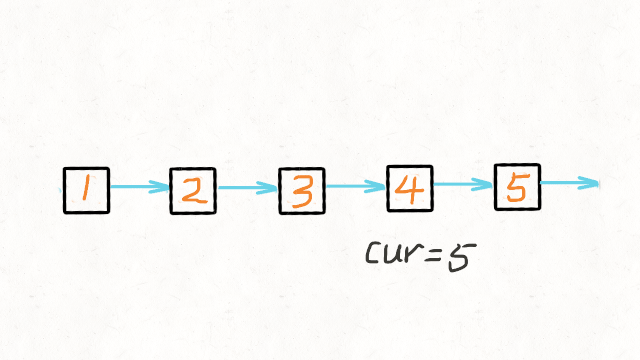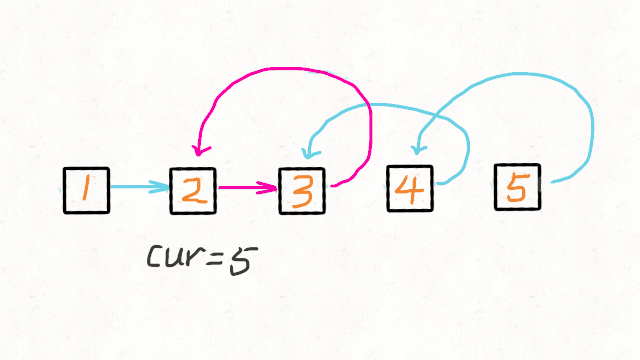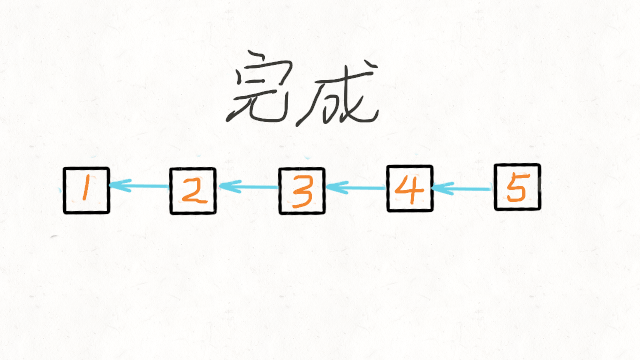
# 这里的cur就是最后一个节点
cur = self.reverseList(head.next)
# 如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5,那么此时的cur就是5
# 而head是4,head的下一个是5,下下一个是空
# 所以head.next.next 就是5->4
head.next.next = head
# 防止链表循环,需要将head.next设置为空
head.next = None
# 每层递归函数都返回cur,也就是最后一个节点
return cur
leetcode 234: 回文链表
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
输入: 1->2 输出: false
输入: 1->2->2->1 输出: true 进阶: 你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
- 解法一:使用额外空间存储链表值再进行比较,时$O(n)$,空$O(n)$
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
vals = []
while head:
vals.append(head.val)
head = head.next
return vals == vals[::-1]
- 解法二:递归,使用递归可以从尾向头进行遍历,结合一个从head开始从头到尾的指针进行比较判断是否是回文。时$O(n)$,空$O(n)$。
- 我们要理解计算机如何运行递归函数,在一个函数中调用一个函数时,计算机需要在进入被调用函数之前跟踪它在当前函数中的位置(以及任何局部变量的值),通过运行时存放在堆栈中来实现(堆栈帧)。在堆栈中存放好了数据后就可以进入被调用的函数。在完成被调用函数之后,他会弹出堆栈顶部元素,以恢复在进行函数调用之前所在的函数。在进行回文检查之前,递归函数将在堆栈中创建 n 个堆栈帧,计算机会逐个弹出进行处理。所以在使用递归时要考虑堆栈的使用情况。
#front从前向后,递归从尾到前,逐个比较
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
self.front = head
def recursive_check(currentNode):
if currentNode is not None:
if not recursive_check(currentNode.next):
return False
if currentNode.val != self.front.val:
return False
self.front = self.front.next
return True
return recursive_check(head)
-
解法三:避免使用 O(n) 额外空间的方法就是改变输入。
我们可以将链表的后半部分反转(修改链表结构),然后将前半部分和后半部分进行比较。比较完成后我们应该将链表恢复原样。虽然不需要恢复也能通过测试用例,因为使用该函数的人不希望链表结构被更改。
- 找到前半部分链表的尾节点。可以使用快慢指针在一次遍历中找到:慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,快慢指针同时出发。当快指针移动到链表的末尾时,慢指针到链表的中间。通过慢指针将链表分为两部分。
- 反转后半部分链表。
- 判断是否为回文。当后半部分到达末尾则比较完成,可以忽略计数情况中的中间节点。
- 恢复链表。
- 返回结果。
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if head is None:
return True
#get mid
pslow,pfast = head,head
while pfast.next and pfast.next.next:
pslow = pslow.next
pfast = pfast.next.next
second_half_start = self.reverseList(pslow.next)
#compare
second_position = second_half_start
while second_position:
if head.val != second_position.val:
return False
head = head.next
second_position = second_position.next
#restore
pslow.next = self.reverseList(second_half_start)
return True
def reverseList(self,head):
result = None
while head:
nextNode = head.next
head.next = result
result = head
head = nextNode
return result
leetcode 237: 删除链表中的节点
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
输出: [4,5,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
说明:
链表至少包含两个节点。 链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。 给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。 不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
- 给定的是节点而不是head指针,无法寻找其前面的节点,因此选择交换下一个结点的值,然后删除下一个节点。
class Solution:
def deleteNode(self, node):
node.val,node.next.val = node.next.val,node.val
node.next = node.next.next
leetcode 83: 删除排序链表中重复的节点
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
- 思路:同之前的删除重复算法,是其简化版。
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return head
p = head
while p:
if p.next and p.val == p.next.val:
while p.next and p.val == p.next.val:
p.next = p.next.next
p = p.next
return head
leetcode 203: 移除链表元素
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
输出: 1->2->3->4->5
- 思路:当要删除的节点在中间时可以很方便地通过链表操作完成,但当链表开始有一个或多个val存在时删除起来比较麻烦,因此可以添加一个新的链表头,最后返回时再取其next。
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return None
result = ListNode(0)
result.next = head
pre,cur = result,result.next
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
pre.next = cur.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return result.next
*leetcode 92:反转链表2
[**中等 **] 反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
- 思路一:使用两个指针分别指向m和n位置,然后逐个进行值的交换。而在n处的指针无法向前移动,因而采用递归的方法。使用left,right两个指针在递归过程中移动,在递归函数中使用头递归的思路,前半段不断移动left和right指针指到m和n的位置,递归后是对left和right位置数据的交换。

class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
if not head:
return None
left, right = head, head
stop = False
def recurseAndReverse(right, m, n):
#重要,保证在right随着递归更新时left也得到更新 而不是产生作用范围内的值
nonlocal left, stop
# base case. Don't proceed any further
#n = 1 , m = 1 ,指向同样的位置,不用交换
if n == 1:
return
#forward过程,left和right指针分别走向对应的m、n位置
# Keep moving the right pointer one step forward until (n == 1)
right = right.next
# Keep moving left pointer to the right until we reach the proper node
# from where the reversal is to start.
if m > 1:
left = left.next
# Recurse with m and n reduced.
#上面right走了一步,m和n对应的位置减一
recurseAndReverse(right, m - 1, n - 1)
# In case both the pointers cross each other or become equal, we
# stop i.e. don't swap data any further. We are done reversing at this
# point.
#right到n处节点位置,开始进行交换操作。判断是不是已经完成交换可以中止。
if left == right or right.next == left:
stop = True
# Until the boolean stop is false, swap data between the two pointers
if not stop:
left.val, right.val = right.val, left.val
# Move left one step to the right.
# The right pointer moves one step back via backtracking.
left = left.next
recurseAndReverse(right, m, n)
return head
- 思路二:使用迭代法改变next指针域,为方便连接,需要额外的指针con来存储m-1处的地址,最后使用con连接n处的节点,也需要tail指针指向m来完成连接n+1处的节点,而在m到n处节点反转的过程可以通过几个指针从前往后迭代完成。
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
if head is None:
return None
prev,curr = None,head
#迭代使curr指向第一个要反转的节点m处
while m > 1:
prev = curr
curr = curr.next
m,n = m-1,n-1
#con用来连接反转后的头prev,tail.next连接n+1处节点
con,tail = prev,curr
#cur应走到n+1的位置方便连接
while n > 0:
nex = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = nex
n -= 1
#建立con与新的子链表头prev以及tail与cur之间的连接
#m = 1 condition
if con:
con.next = prev
else:
head = prev
tail.next = curr
return head
leetcode 86: 链表划分
[中等]Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Input: head = 1->4->3->2->5->2, x = 3
Output: 1->2->2->4->3->5
- 思路:使用两个指针,分别连接小于x和大于等于x的节点,之后再将两个链表进行连接。
- 注意点:为方便处理开头大于x的情况,使用空头节点。
- 在较大值链表最后需要指定next=None,不然会导致无限循环致使超时。
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, head, x):
before = before_head = ListNode(0)
after = after_head = ListNode(0)
while head:
if head.val < x:
before.next = head
before = before.next
else:
after.next = head
after = after.next
head = head.next
# Last node of "after" list would also be ending node of the reformed list
after.next = None
# 连接两个链表
before.next = after_head.next
return before_head.next
leetcode 2: 两数相加
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807
- 两个链表同时遍历,逐个相加,注意用一个变量来计算进位值。
- 注意:循环结束条件:两个链表都为空且进位为零。
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
q = result = ListNode(0)
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry!=0 :
val1 = l1.val if l1 else 0
val2 = l2.val if l2 else 0
q.next = ListNode((val1+val2+carry)%10)
q = q.next
carry = (val1+val2+carry)//10
l1 = l1.next if l1 else None
l2 = l2.next if l2 else None
return result.next
leetcode 445: 两数相加2
- 相较于上一题,变成了高位在前,使用栈存储数据在同时出栈计算,使用头插入法插入链表节点。
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
stack1 = []
stack2 = []
while l1:
stack1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
stack2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
result = ListNode(0)
carry = 0
while len(stack1)>0 or len(stack2) > 0 or carry != 0 :
val1 = stack1.pop() if len(stack1) > 0 else 0
val2 = stack2.pop() if len(stack2) > 0 else 0
node = ListNode((val1+val2+carry)%10)
node.next = result.next
result.next = node
carry = (val1+val2+carry)//10
return result.next
*leetcode 148:排序链表
[中等较难]Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
-
思路:根据时空复杂度的要求,选用归并排序,因为要求$O(1)$的空间复杂度,不能使用递归方法。(二分的递归方法空间复杂度$O(logn)$)因而选用从底到顶直接合并的方法。
-
附:使用递归方法的链表归并排序方法:
- 分割 cut 环节: 找到当前链表中点,并从中点将链表断开(以便在下次递归 cut 时,链表片段拥有正确边界);
- 我们使用fast,slow 快慢双指针法,奇数个节点找到中点,偶数个节点找到中心左边的节点。
- 找到中点 slow 后,执行 slow.next = None 将链表切断。
- 递归分割时,输入当前链表左端点 head 和中心节点 slow 的下一个节点 tmp(因为链表是从 slow 切断的)。
- cut 递归终止条件: 当head.next == None时,说明只有一个节点了,直接返回此节点。
- 合并 merge 环节: 将两个排序链表合并,转化为一个排序链表。
- 双指针法合并,建立辅助ListNode h 作为头部。
- 设置两指针 left, right 分别指向两链表头部,比较两指针处节点值大小,由小到大加入合并链表头部,指针交替前进,直至添加完两个链表。
- 返回辅助ListNode h 作为头部的下个节点 h.next。
- 时间复杂度 O(l + r),l, r 分别代表两个链表长度。
- 当题目输入的 head == None 时,直接返回None。
class Solution: def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: if not head or not head.next: return head #快慢指针寻找中间结点,这个中间结点不必是严格定义的中间 slow,fast = head,head.next while fast and fast.next: fast = fast.next.next slow = slow.next #cut 分治 mid,slow.next = slow.next,None left,right = self.sortList(head),self.sortList(mid) #排序 插入到新链表 h = result = ListNode(0) while left and right: if left.val < right.val: h.next = left left = left.next else: h.next = right right = right.next h = h.next h.next = left if left else right return result.next - 分割 cut 环节: 找到当前链表中点,并从中点将链表断开(以便在下次递归 cut 时,链表片段拥有正确边界);
-
迭代法:
- 以inv=1为步长,每次找两个inv长度的子链表进行归并。注意要通过遍历来得到两个子链表的头h1、h2,以及其对应的长度len1、len2,不能用next指针来判断子链表的结束。
- 到达链表末尾后,inv*=2,模拟第二轮归并过程。
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
result = ListNode(0)
result.next = head
q = head
length = 0
while q:
q = q.next
length += 1
inv = 1
#最后一轮 整个链表长度为inv 结束循环
while inv < length:
#pre在归并过程中充当每次归并的头节点
pre = result
h = result.next
#用inv不断切分原链表(每次两个子链表)并进行归并
while h:
#h1为第一个归并子链表表头,i用来计算子链表长度inv
h1 = h
i = inv
while h and i:
h = h.next
i -= 1
#还未达到inv长度时上面的循环中止,本轮归并完成
if i:
break
h2 = h
#接下来继续向下,计算第二个归并子链表长度,并方便下一组归并子链表。
i = inv
while h and i:
h = h.next
i -= 1
#两个归并子链表的长度,这里不能用指针为空来判定,因而上面需要计算出两个子链表长度
len1,len2 = inv,inv-i
#对两个归并子链表进行排序
while len1 and len2:
if h1.val < h2.val:
pre.next = h1
h1 = h1.next
len1 -= 1
else:
pre.next = h2
h2 = h2.next
len2 -= 1
pre = pre.next
pre.next = h1 if len1 else h2
#接下来将pre指向下一轮归并子链表的位置
while len1 > 0 or len2 > 0 :
pre = pre.next
len1 -= 1
len2 -= 1
#链接原链表
pre.next = h
inv *= 2
return result.next
leetcode 328: 奇偶链表
- 类似于上面的链表划分题,使用两个哑节点分别连接对应的奇偶节点,最后连接。
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next :
return head
odd_head = odd = ListNode(0)
even_head = even = ListNode(0)
val = 1
p = head
while p:
if val % 2 != 0:
odd_head.next = p
odd_head = odd_head.next
else:
even_head.next = p
even_head = even_head.next
p = p.next
val += 1
even_head.next = p
odd_head.next = even.next
return odd.next
leetcode 24: 两两交换链表中的节点
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
- 设立一个哑节点,遍历链表并每两个进行一次交换。
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
res = result = ListNode(0)
res.next = head
while res.next and res.next.next:
a,b = res.next,res.next.next
res.next = b
a.next = b.next
b.next = a
res = res.next.next
return result.next
leetcode 147: 对链表进行插入排序
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
- 添加哑节点,然后逐个节点遍历,并与之前排好序的进行比较。
- 为节省时间(序列呈升序时),使用tail指针指向已排好序的链表尾,先与尾节点进行比较,小于尾节点时再从头进行比较。
- 遇到链表交换问题时,注意最后一个结点之后连接的还是不是None,可能导致循环超时。
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
while not head or not head.next:
return head
res = ListNode(0)
res.next = head
#加一个tail指针,指向排好序的队尾,对升序序列节约时间,且可最后设定tail.next = None
tail = head
head = head.next
while head:
if head.val >= tail.val:
tail.next = head
tail = tail.next
head = head.next
else:
#两个指针 用于比较和插入
p,q = res,res.next
while q.val <= head.val and q!=tail:
p,q = p.next,q.next
#insert after p
next_node = head.next
p.next = head
head.next = q
head = next_node
tail.next = None
return res.next
leetcode 19: 删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点
Given a linked list, remove the n-th node from the end of list and return its head.
Example:
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
Note:
Given n will always be valid.
- 添加哑节点(删除的是第一个节点),然后使用双指针同时遍历
- 注意:进行删除时需要知道倒数n+1个节点,因此两个指针的距离不是n而是n+1。
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
res = ListNode(0)
res.next = head
p,q = res,res
for i in range(n+1):
#若是删除第一个节点时q会直接到None,而n==i
if not q:
return head if i!=n else head.next
q = q.next
while q:
p,q = p.next,q.next
p.next = p.next.next
return res.next
leetcode 61: 旋转链表
Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
- 思路一:按数学的思路,把右移操作化为左移
- 先循环计算出链表长度l,并把链表变为循环链表;
- 根据需要把尾部放到头部的操作次数计算出从头部到新的头部的操作次数:length - k%length,其前一个节点为新的尾节点;
- 尾节点设定next指针域,并返回新的头节点。
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
length = 1
q = head
while q.next:
q = q.next
length += 1
q.next = head
#得到移位后的尾节点,下一个节点为新头节点
dist = length - k%length -1
for _ in range(dist):
head = head.next
next_node = head.next
head.next = None
return next_node
- 思路二:双指针遍历找到需要截取的位置,然后把后面截掉的部分放在前面组合为新链表。
- 不合适:k的值可能大于length,双链表法没法直接获取链表长度,需单独写一个遍历获得长度,略显麻烦。
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
q , length= head,0
while q:
q,length =q.next,length+1
rel_k = k % length
p,q = head,head
#p in new end , set next = None
for _ in range(rel_k):
q = q.next
#终止条件用q.next,这样最终q会在最后一个节点,q再需要截断的结点之前。
while q.next:
p ,q = p.next,q.next
q.next = head
next_node = p.next
p.next = None
return next_node
leetcode 143: 重排链表
Given a singly linked list
L: L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln,
reorder it to: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Example 1:
Given 1->2->3->4, reorder it to 1->4->2->3.
Example 2:
Given 1->2->3->4->5, reorder it to 1->5->2->4->3.
- 思路一 迭代配合递归,左边left迭代,右边使用递归,直到相等。
- 注意:和上面交换结点的题不一样,在有奇数和偶数节点时有不同的处理。
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
res = result = ListNode(0)
left,right = head,head
stop = False
def recursive_reorder(right):
nonlocal left,stop,res
if not right:
return
recursive_reorder(right.next)
#偶数个节点 中止
if right.next == left:
stop = True
#奇数个节点,把该节点连接上
if left == right:
stop = True
res.next = left
res = res.next
if not stop:
res.next = left
left = left.next
res.next.next = right
res = res.next.next
res.next = None
recursive_reorder(head)
- 思路二:后半部分入栈,和前半部分同步进行插入。同样需要注意奇数时最中间结点的问题。
- 不推荐,使用快慢指针需要严格找到中间节点。
- 更新版思路:对全部链表入栈,同时可以计算出链表的长度l,一边遍历原链表一边出栈进行$floor(l/2)$次,然后如果$l$是奇数多出栈一个元素。
class Solution:
def reorderList(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
stack = []
p,length = head,0
while p:
stack.append(p)
p , length = p.next , length + 1
res = ListNode(0)
for _ in range(length//2):
res.next = head
head = head.next
res.next.next = stack.pop()
res = res.next.next
if length % 2 == 1:
res.next = stack.pop()
res = res.next
res.next = None
*leetcode 23: 合并 k 个有序链表
[困难]Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
Example:
Input:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
- 思路一 暴力法:遍历k个数组,将其值存入一个数组中,再进行排序,之后将排序后的值对一个新的链表进行赋值。 $O(NlogN),O(N)$
- 当要求in-place进行排序,不能新建链表节点时不能使用。
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
vals = []
for li in lists:
while li:
vals.append(li.val)
li = li.next
vals.sort()
res = result = ListNode(0)
for val in vals:
result.next = ListNode(val)
result = result.next
return res.next
- 思路二 类似于两个排序链表的合并,同时对k个进行合并,每轮比较k个值取最小的。$O(kN)$
- 注意:停止判定不能用指针为空,而应该以该轮是不是有新的节点插入为终止条件。
- 测试样例k过大,每个链表一个元素,退化为$O(N^2)$,算法超时
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
res = result = ListNode(0)
loop = True
while loop:
min_val = 1000000
min_idx = -1
for i,h in enumerate(lists):
if h and h.val < min_val:
min_val = h.val
min_idx = i
#add minist to res
if min_idx != -1:
res.next = lists[min_idx]
lists[min_idx] = lists[min_idx].next
res = res.next
else:
loop = False
res.next = None
return result.next
- 思路三 优先队列
- 优先队列:根据优先级来判断是否先出。相当于对list的每个元素加了一个优先级的关键词。
- 相关库:heapq,默认为小根堆,函数:heapq.heappush和heap.heappop
- queue.PriorityQueue 函数:put , get.
- 优先队列接受内容:元组,(priority,content) 注意:元组两个值都要可比较才行,第二个元素应该存lists的索引
- 算法流程:
- 把所有的链表都放入优先队列中,使用最小堆来高效完成k个值的比较,
- 将头节点值最小的链表弹出,
- 将该节点连接到排好序的节点后面,然后把下一个节点在放入优先队列。
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
from queue import PriorityQueue
res = result = ListNode(0)
q = PriorityQueue()
for i in range(len(lists)):
if lists[i]:
q.put((lists[i].val,i))
while not q.empty():
val,i = q.get()
res.next = lists[i]
res = res.next
lists[i] = lists[i].next
if lists[i]:
q.put((lists[i].val,i))
return result.next
- 思路四 分治
- 将k个链表配对并将同一对中的链表合并。
- 第一轮合并以后,k 个链表被合并成了 $\frac{k}{2}$个链表,平均长度为 $\frac{2N}{k}$,然后是 $\frac{k}{4}$个链表, $\frac{k}{8}$个链表等等。
- 重复这一过程,直到我们得到了最终的有序链表。
- 注意循环范围的写法
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:
inter = 1
amount = len(lists)
while inter < amount:
for i in range(0,amount - inter,inter*2):
lists[i] = self.merge(lists[i],lists[i+inter])
inter *= 2
return lists[0] if amount > 0 else lists
def merge(self,l1,l2):
head = point = ListNode(0)
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
point.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
point.next = l2
l2 = l1
l1 = point.next.next
point = point.next
if not l1:
point.next=l2
else:
point.next=l1
return head.next
*leetcode 25: k 个一组翻转链表
困难Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
Example:
Given this linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
For k = 2, you should return: 2->1->4->3->5
For k = 3, you should return: 3->2->1->4->5
Note:
- Only constant extra memory is allowed.
- You may not alter the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
- 思路:由于要求不需要额外的空间,栈和递归方法不能使用。因此使用双指针,一边遍历,每达到k个节点进行一次头插入。
class Solution(object):
def reverseKGroup(self, head, k):
if not head :
return head
res = result = ListNode(0)
res.next = head
while res:
pre = res
count = k
while res and count:
res = res.next
count -= 1
#还够一次反转的k个值
if res:
stop = res.next if res.next else None
#保存反转后的尾节点,便于和之后的链表连接
new_tail = pre.next
q = pre.next
while q != stop:
next_node = q.next
q.next = pre.next
pre.next = q
q = next_node
#连接之后的节点
new_tail.next = stop
#重设下一轮的节点遍历,为上一轮反转后的尾节点
res = new_tail
return result.next